As you know Drupal 8 was released on Nov 19 / 2015 (finally).
One of the most recurrent questions is “It’s time to create new projects in Drupal 8”, but there is another difficult question. “How I can migrate my current Drupal 7/6/* to Drupal 8”
To try to answer that question let me explain a little bit how Migration works in Drupal 8.
Modules required
Drupal 8 provides in their core modules the Migrate module; this module provides a mini-framework to be used to migrate from Any source to Drupal 8. I said ANY because this module itself doesn’t have any logic related to Drupal stuff.
The idea is if you plan to migrate from a specific source like Drupal, Wordpress, CQ5, etc. You must write an integration to handle the transformation of content into Drupal 8 structure.
Fortunately for us at least we have a Drupal 8 core module related to Drupal named Migrate Drupal, this module contains some Migrate plugin to run the migration process between older Drupal versions to Drupal 8, but this module doesn’t include migration definitions since Drupal 8 beta 13
Therefore, the first step you need to do is install these modules, I will use the project Drupal Console for this tasks and I will continue using some commands available related with migration.
$ drupal module:install migrate migrate_drupalWhere I can find migrations
After installing modules Migration and Migrate Drupal, I guess you are waiting for something in UI to start to handle your migrations. Sadly there is nothing inside Drupal Core to provide a UI for migration, this responsibility relies on two contributed modules Migrate Plus and Migrate Upgrade.
Each module applies a different point of view about migrations, both IMHO looks like Migrate Upgrade it’s in a more mature state. But, there is always a but, I don’t like the idea that you are only available to see all migrations available when you are running the migration itself.
With Drupal just released it’s probably that you will be in a stage where you don’t know what are you doing, so I decided to implement some migration command inside Drupal Console project with my point of view.
Loading migrations
As I said before, I prefer load migrations but without running a migration yet. For that purpose, I did a command migrate:setup as you can see in following CLI execution sample.
$ drupal migrate:setup --db-type=mysql --db-host=127.0.0.1 \
--db-name=plato_tipico --db-user=root --db-pass=root \
--db-port=3306 --no-interactionIn the sample above I pass all parameters using inline mode, but if you omit an option, the command will start the interactive mode. Remember to remove the option *–no-interaction** to enable the interactive mode.
The command above will inspect your legacy DB and import all migrations available in Drupal 8 to be used with your legacy DB.
All migration entities created will remain in your system, even after completing a migration process.
Get a list of migrations
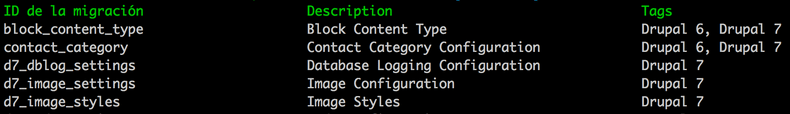
To get a list of migrations available in your system, you must execute the following command
$ drupal migrate:debugAs you can appreciate in the following image, some migrations work in more that one Drupal legacy version.
Execute a migration
After reviewing your system in term of migrations available, we could execute all migrations available for your legacy system you can run the following command to start a full migration process.
$ drupal migrate:execute all --db-type=mysql --db-host=127.0.0.1 \
--db-name=plato_tipico --db-user=root --db-pass=root \
--db-port=3306 --no-interactionBelow you can see how looks the migration process.
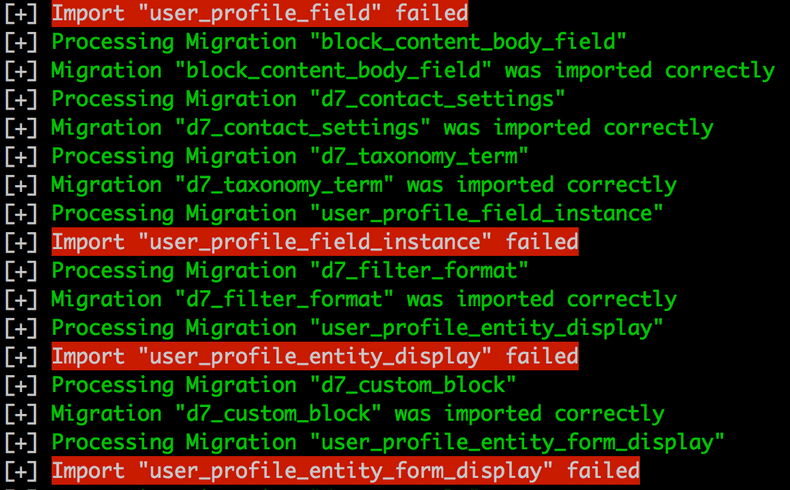
The image above shows how the command report what migrations fail and what migration works. As you can see each migration is independent and the migration process is not interrupted if some of them fail.
But if you want to avoid to execute one or more migrations to prevent any exception you can use the parameter –exclude providing the migration id(s) do you want to exclude, you can get those ids from migrate:debug command.
Moreover, if you only want to execute one or a couple of migrations, just change the parameter all for any migration id(s) do you want, this is useful to perform a partial migration after resolve any issues found after executing a full migration process
Where are located migrations?
Now you are wondering “Where are located migration” if they aren’t in Migrate or Migrate Drupal. Well, migrations are allocated in each specific module, for instance, if you review in your Drupal Core modules in path /core/modules/book/migration_templates you will find some YAML files with the information necessary to create a Migration entity in your system. When you executed the command migrate:setup all migration_templates folder were parsed to create Migration Entities.
#Caveats Right now there are mostly migrations available for Drupal 6, I guess the bet is related to Drupal 6 are more critical to be migrated to Drupal 8.
You can find more Drupal 7 migration proposed as issues in http://groups.drupal.org/imp sandbox, in Anexus we propose around 70 migration entities for Drupal 7 and 10 of them were already accepted in Drupal 8 core. I promise to provide a list of all our Drupal 7 Migration in few weeks.
I hope you found this article useful.